Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is a subfield of machine learning that combines neural networks with reinforcement learning techniques to make decisions in complex environments. It has been applied in various domains such as game playing, robotic manipulation, and autonomous vehicles.
One of the most fascinating areas of study is the application of deep reinforcement learning. This method of machine learning, which involves rewarding an AI agent for correct actions and punishing it for incorrect ones, has been used in a unique experiment that allows us to watch AI learn to walk. This experiment, which is both intriguing and enlightening, provides a glimpse into the potential future of AI and its applications.
One of the most fascinating areas of study is the application of deep reinforcement learning. This method of machine learning, which involves rewarding an AI agent for correct actions and punishing it for incorrect ones, has been used in a unique experiment that allows us to watch AI learn to walk. This experiment, which is both intriguing and enlightening, provides a glimpse into the potential future of AI and its applications.
AI learns to walk
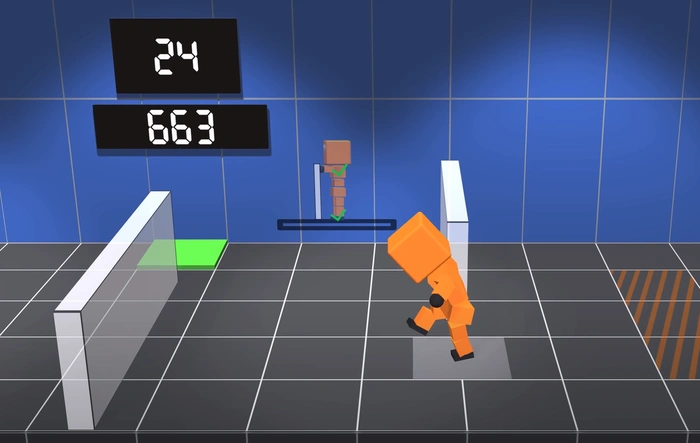
The experiment revolves around an AI named Albert, who is tasked with learning how to walk in order to escape from five different rooms. The rooms, each with their own unique challenges, serve as the training ground for Albert. The AI’s actions are controlled by a neural network, which is updated after each attempt. The goal of these updates is to increase the rewards Albert receives and decrease the punishments, thereby encouraging the AI to learn and adapt.
In the context of walking, the agent is typically a simulated or physical robot with legs as in the example below. The state space includes variables like leg positions, joint angles, and velocity. Actions might correspond to setting torque or force on joints. The reward function could be designed to encourage forward movement while penalizing excessive energy use or falls.
Other articles you may find of interest on the subject of artificial intelligence :
Deep reinforcement learning, the method used to train Albert, is a subset of machine learning that focuses on decision-making. It’s a process that involves an agent, in this case, Albert, interacting with an environment to achieve a certain goal. The agent is rewarded or punished based on its actions, which encourages it to learn from its experiences and make better decisions in the future. This method is particularly effective in teaching AI complex tasks, such as walking, which require a combination of balance, coordination, and decision-making.
Neural network
In the experiment, Albert’s neural network is updated after each attempt to escape the rooms. This update process is crucial to Albert’s learning journey. It allows the AI to reflect on its actions, learn from its mistakes, and make better decisions in the future. Over time, Albert begins to understand the consequences of its actions and learns to navigate the rooms more effectively.
The neural network is like the brain of the system, helping it decide what to do next based on what it currently knows. It uses this “brain” to estimate rules (policy) and predict future benefits (value functions). Different types of neural networks are used based on the kind of information the system gets. For example, if the system uses pictures or video, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are commonly used. If the system needs to remember past actions or events, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are useful.
The design of this “brain” needs to be just right. It has to be sophisticated enough to understand complicated situations and make good decisions, but not so complicated that it becomes too difficult to manage or understand. The experiment is a testament to the power of deep reinforcement learning. It showcases how AI can learn complex tasks through trial and error, much like a human would. Albert’s journey from a novice walker to an adept navigator is a fascinating demonstration of the potential of AI.
This mesmerizing experiment offers a unique glimpse into the world of AI and deep reinforcement learning. Demonstrating how artificial intelligence can learn to walk, adapt to new environments, and make decisions based on past experiences. It’s a fascinating look at the potential of AI, and a reminder of the exciting advancements that are yet to come in this field. As always we will keep you up to speed on everything new in the realm of AI as it happens.
A few more articles you may find of interest on the subject of neural networks :
Filed Under: Guides, Top News
Latest Aboutworldnews Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, Aboutworldnews may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.