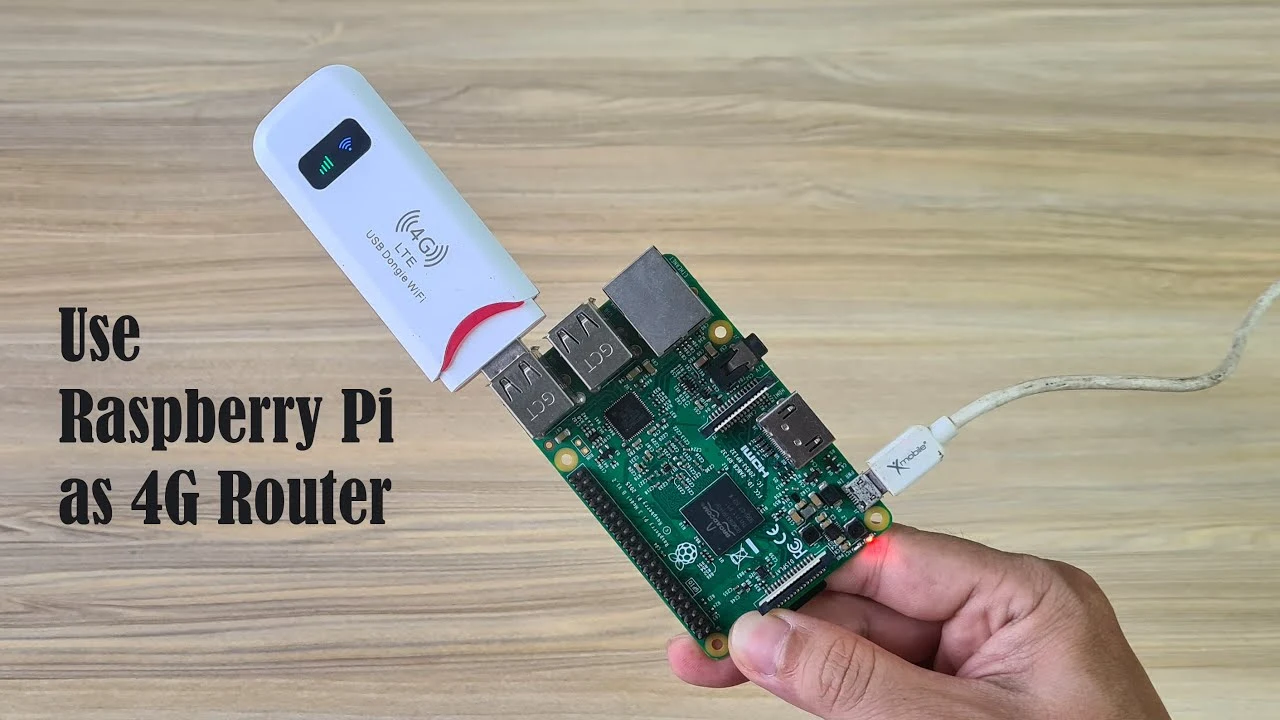
Imagine turning a simple, affordable Raspberry Pi mini PC into a powerful 4G LTE router that can spread high-speed internet to your other projects and devices. By leveraging OpenWRT, an open-source firmware, you can transform your Raspberry Pi into a networking powerhouse, sharing a 4G connection both through cables and wirelessly. Let’s dive into how you can upgrade your Raspberry Pi into a multi-purpose networking device.
The Raspberry Pi is a versatile little computer that can be repurposed as an efficient 4G LTE router. To start, you’ll need a Raspberry Pi, a compatible 4G LTE USB modem, and a SIM card with an active data plan. The goal is to install OpenWRT on the Raspberry Pi, which will manage the 4G connection from the USB modem.
The setup process for creating a Raspberry Pi 4G LTE Router includes :
– Installation of OpenWRT operating system on Raspberry Pi
– Flashing the OpenWRT firmware onto the Raspberry Pi’s memory card
– Inserting a 4G LTE SIM card into a USB Modem and connecting it to the Raspberry Pi
– Configuring OpenWRT settings and setting up a password for security
– Installing additional packages to enable USB Modem connectivity
– Creating a new WAN interface for the LTE 4G USB Modem
– Deleting previous WAN interfaces to ensure the router uses the USB Modem for internet access
– Setting up a wireless network to share the 4G connection with other devices
For developers, OpenWrt serves as a versatile framework, allowing the creation of applications without the necessity of developing an entire firmware. For users, this translates into unparalleled customization potential, empowering them to utilize their devices in innovative ways that surpass original design intentions.
Raspberry Pi 4G LTE Router
The first step is to get the OpenWRT firmware that matches your Raspberry Pi model. You can use a program like Balena Etcher to write this firmware onto your Raspberry Pi’s SD card. Once you’ve flashed the firmware, insert the SD card into your Raspberry Pi and power it up to begin the setup process.
Here are some other articles you may find of interest on the subject of Raspberry Pi 5 :
After OpenWRT is operational, insert the 4G LTE SIM card into the USB modem and connect it to the Raspberry Pi. You might need to add some extra OpenWRT packages to make sure the system can recognize and work with the USB modem properly.
Now, with the modem connected, it’s time to set up OpenWRT to direct internet traffic through it. You’ll need to create a new WAN interface for the USB modem within OpenWRT and make it the preferred route for internet connectivity. It’s also crucial to secure your network by setting a strong password.
The following task is to enable a Wi-Fi network on your Raspberry Pi. You’ll configure the wireless settings within the OpenWRT interface, including the network name (SSID) and security encryption. This allows other devices to connect to your newly created 4G LTE router.
Once everything is configured, you should test your Raspberry Pi router. Connect a device to the Wi-Fi network and check if you can access the internet. If you can browse online, your Raspberry Pi is now successfully functioning as a 4G LTE router.
With a Raspberry Pi and OpenWRT, you can craft a custom 4G LTE router that offers internet access to various devices. This setup is particularly useful in areas where broadband access is scarce, providing a dependable internet connection wherever mobile network coverage is available.
Image Credit : NETVN82
Filed Under: DIY Projects, Top News
Latest aboutworldnews Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, aboutworldnews may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.