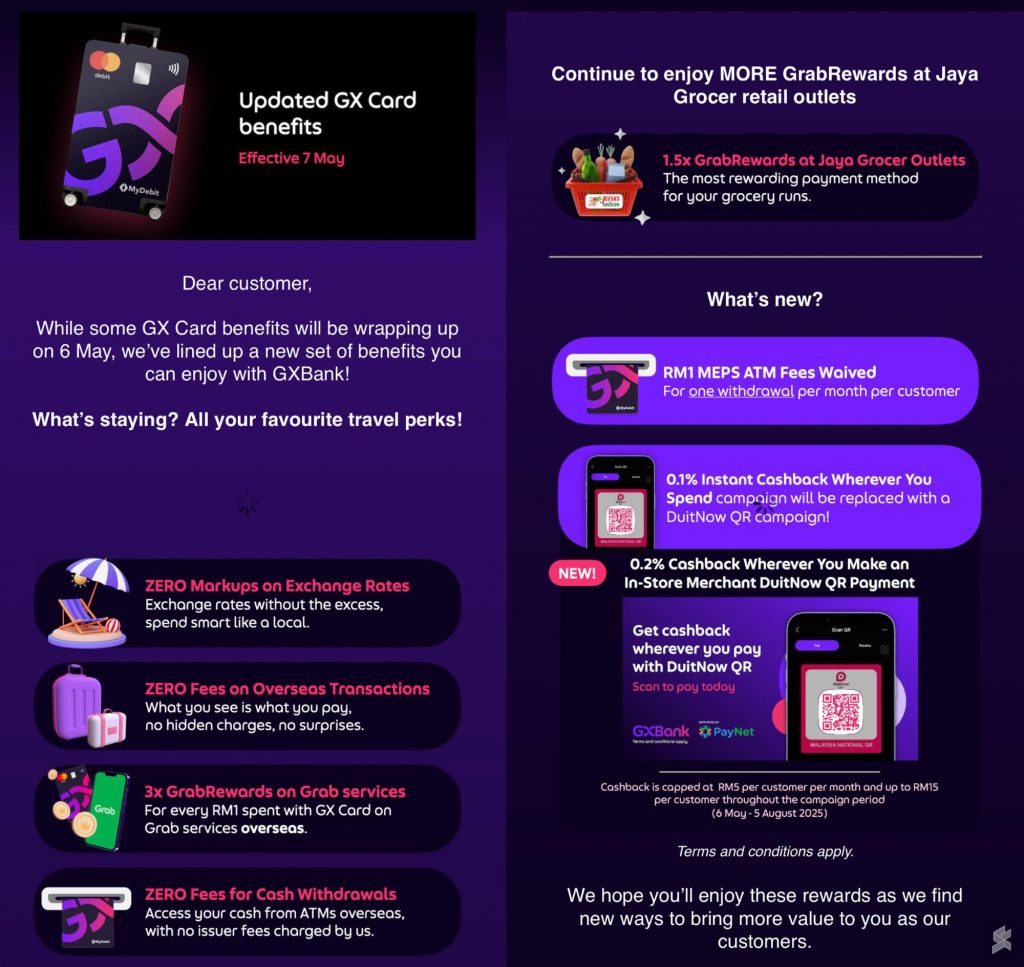
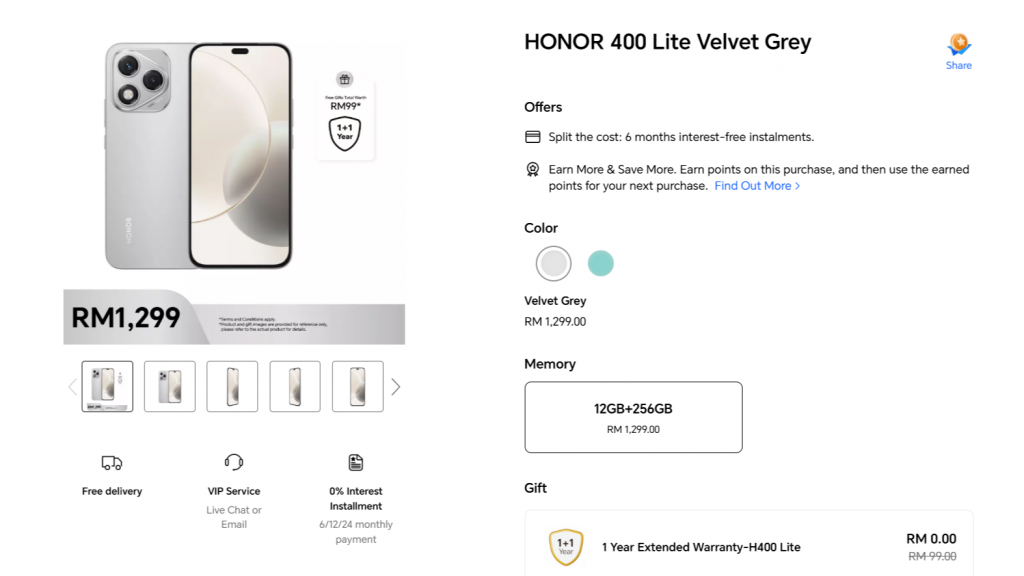
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks. They aim to track the performance of a specific index, sector, commodity, or asset class. ETFs offer diversification benefits of mutual funds while also providing real-time trading flexibility.
ETFs or Exchange-Traded Funds are crucial in investment as they offer diversified exposure to a specific area of the market, effectively reducing risk. They are highly liquid, which allows flexibility and ease in trading. Importantly, ETF investment often have lower expense ratios, making them a cost-effective investment strategy.
Benefits of Investing in ETFs
Diversification of an investment portfolio is a risk management strategy, involving the allocation of capital across various financial instruments, industries, and other categories. It reduces exposure to a single asset, thus safeguarding investments against market volatility and unexpected downturns. In essence, diversification helps minimize risk while maximizing returns.
Cost efficiency refers to the balance between the cost of production and the value of output. It’s a key factor for businesses aiming to gain a competitive advantage by optimizing their resource usage. A cost-efficient operation produces the highest possible output at the least possible cost, maximizing profitability.
Flexibility in trading refers to the ability of a trader to adapt their strategies and decisions based on market changes. It embodies versatility and resilience, allowing traders to manoeuvre through varying conditions, whether it’s fluctuating prices, changing trends, or evolving economic landscapes. Thus, it’s crucial for successful trading.
Transparency in holdings refers to the full disclosure, clarity, and accountability of assets owned by an individual or company. This information, often publicly available, is crucial for enhancing trust among stakeholders. It promotes ethical practices, reduces corruption, and ensures fair business transactions.
Basics of ETF Investment
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are a popular type of investment vehicle. They come in various types, including bond ETFs, which invest in bonds; industry ETFs, targeting a specific industry such as technology or healthcare; commodity ETFs, which focus on commodities like gold or oil; and international ETFs, offering exposure to foreign markets.
Determining the right ETF requires an understanding of your risk tolerance and investment goals. Lower-risk options such as bond ETFs may suit conservative investors. Alternatively, those willing to accept larger risks for potentially higher returns might prefer sector-specific or emerging markets ETFs. Always assess the ETF’s historical performance, fees, and diversification level.
Understanding expense ratios is crucial for investors as they can significantly impact returns. These ratios represent the percentage of a fund’s assets used for administrative and other operating expenses. A high expense ratio can erode earnings over time, diminishing an investment’s overall profitability.
The role of the ETF’s underlying index is crucial as it serves as a benchmark for the fund’s performance. The index includes a selection of securities that the ETF aims to replicate in terms of performance and yield. Understanding this role is vital for informed investment decisions and risk assessment.
Steps to Investing in ETFs
Opening a brokerage account is a crucial step towards investing in the stock market. It acts as a platform that links you with various trade options such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The process involves choosing a reliable broker, filling out an application form, and depositing funds.
Researching ETFs involves analysis of their historical performance, associated management fees, and underlying assets. Understanding the sectors or markets they expose investors to is also critical. It’s important to balance performance potential with risk tolerance and long-term investment goals while exploring different ETF options.
Purchasing exchange-traded funds (ETFs) allows investors to diversify their portfolios without buying each security. These ETFs, traded on stock exchanges, encompass multiple stocks, assets, or bonds. Their prices fluctuate throughout the day, offering potential for both short-term and long-term gains.
Monitoring and re-balancing your ETF portfolio is crucial for maintaining your investment strategy and risk tolerance. This involves keeping track of the performance of individual ETFs, comparing them to their benchmark indices, and making adjustments as needed to align with your financial goals.
Risks Associated with ETF Investment
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to potential losses caused by factors that affect the performance of the overall financial market. Examples of such factors encompass interest rate changes, inflation, political instability, or global events. It is non-diversifiable and impacts all industries and companies in the market.
Tracking error risk relates to the deviation of the performance of an investment portfolio or a fund from the benchmark it is intended to track. It indicates the inconsistency between the behaviour of the portfolio and the benchmark, possibly affecting the overall investment returns.
Liquidity risk refers to a situation where an individual or company is unable to meet short-term financial demands. This typically occurs due to the inability to convert assets into cash without a significant loss in value. It exposes businesses to losses and potential bankruptcy if not managed properly.
Currency risk, also known as exchange rate risk, is a form of financial risk that arises from a potential change in the exchange rates between two currencies. It may lead to significant losses for businesses and investors involved in international trade or investment, affecting their financial performance and stability.
Strategies for Successful ETF Investment
Dollar-cost averaging is an investment strategy where a fixed amount of money is consistently invested in a particular asset over regular intervals, irrespective of its price. This approach dilutes the impact of market volatility and can lower the average cost per share over time.
Investing in broad-market ETFs is a secure strategy for diversifying your investment portfolio. These Exchange Traded Funds mirror the performance of a specific market index, spreading risk across various sectors. For long-term investors, they can be a stable, low-cost alternative to individual stocks.
Diversifying across different asset classes is a smart investment strategy that mitigates risk and enhances return potential. It involves spreading investments across various asset categories, such as equities, bonds, real estate, cash, or commodities. By doing so, investors create a well-balanced portfolio, reducing financial exposure to any single asset class.
Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments are integral for successful investment management. This allows for the timely identification of any underperforming investments and the reallocation of assets to maintain a balanced portfolio. It helps in optimizing returns, managing risks, and meeting your changing financial goals.