Reducing energy costs is a priority for many households and businesses, particularly in times of rising utility prices. Standard and off-grid solutions offer a sustainable and cost-effective way to address this challenge.
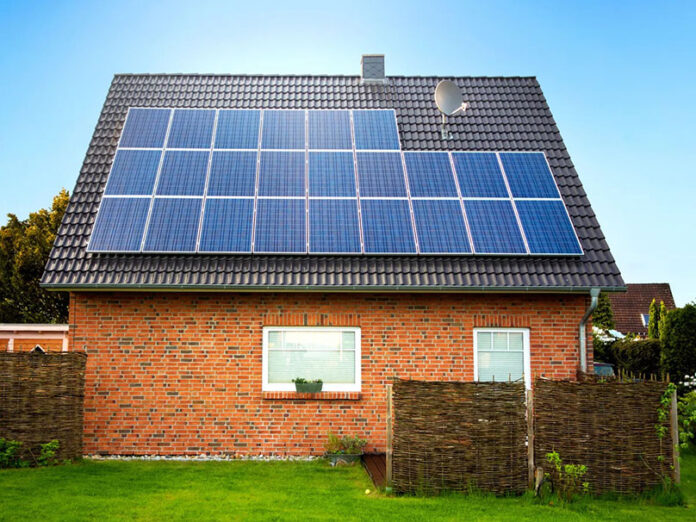
By harnessing the power of the sun, solar energy systems provide a renewable energy source that can significantly cut down on electricity bills. As technology advances and the adoption of renewable energy increases, the benefits of solar power are becoming more accessible to the general public.
Off-grid systems are an innovative solution for those looking to further optimize their energy savings. Unlike traditional grid-tied systems, off-grid solar panel system operate independently of the local utility grid, providing energy autonomy.
This independence not only reduces energy costs but also allows individuals to earn money by selling excess energy back to the grid or by using it to power additional systems. The flexibility and financial benefits of off-grid solar solutions make them an attractive option for those seeking to reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources.
Let’s Start With Basics


Solar power is derived from converting sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells are made from semiconductor materials that generate electric currents when exposed to sunlight. The generated electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other facilities. Solar power systems can be installed on rooftops or in open areas with sufficient sunlight exposure.
Key Components
- Panels: These are the primary components that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. They are typically made of silicon and come in various types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels.
- Inverter: This device converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the standard electrical current used in most homes and businesses.
- Battery Storage: Batteries store excess electricity generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight. This ensures a continuous power supply even when the sun isn’t shining.
- Charge Controller: This regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to prevent overcharging and damage to the batteries.
- Mounting System: Solar panels are installed on a mounting system that secures them to rooftops or the ground, ensuring optimal orientation and angle for maximum sunlight exposure.
Benefits
- Reduced Electricity Bills: By generating your own electricity, you can significantly lower your utility bills. Any excess energy can be sold back to the grid, further reducing costs.
- Environmental Impact: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Solar power provides a degree of energy independence, reducing vulnerability to utility price increases and power outages.
- Increased Property Value: Homes and businesses with solar power systems typically have higher property values due to the long-term savings and sustainability features.
Off-Grid Systems
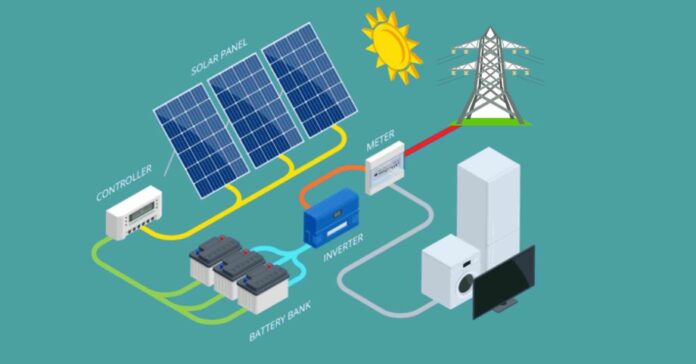

Off-grid systems are designed to operate independently of the traditional utility grid. This setup is ideal for remote locations where grid access is limited or unavailable. It is also beneficial for those looking to achieve complete energy independence.
Components of an Off-Grid System
An off-grid system includes similar components to a grid-tied system but with additional features for self-sufficiency:
- Panels: Capture and convert sunlight into electricity.
- Battery Storage: Stores excess energy for use during non-sunny periods.
- Inverter: Converts DC to AC for household use.
- Backup Generator: Provides additional power during extended periods of low sunlight.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of energy to and from the batteries to prevent overcharging.
Advantages of Off-Grid Systems
- Energy Autonomy: Off-grid systems provide complete independence from the utility grid, making them ideal for remote locations or for those who want to be self-sufficient.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment may be higher, off-grid systems can save money in the long run by eliminating utility bills.
- Environmental Benefits: Off-grid systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprints.
- Earning Potential: Users can sell excess energy or utilize it to power additional equipment, creating an opportunity for revenue generation.
Financial Benefits


Investing in solar and off-grid solutions can provide substantial financial benefits. Here are some ways these systems can reduce energy costs and even generate income:
Tax Incentives and Rebates
Many governments offer tax incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of renewable energy systems. These financial incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs of installing solar and off-grid systems. In some regions, homeowners can receive a federal tax credit for a percentage of the installation costs, making solar power more affordable.
Net Metering
Net metering allows homeowners and businesses with grid-tied solar systems to sell excess electricity back to the utility grid. This process credits the energy produced by the solar panels against the energy consumed from the grid, reducing overall electricity bills.
In some cases, net metering can result in a negative electricity bill, meaning the utility company pays the homeowner for the excess energy generated.
Long-Term Savings
While the initial investment in standard and off-grid systems can be substantial, the long-term savings are significant. Solar panels have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, during which they generate free electricity. The savings on utility bills over this period can offset the initial costs, resulting in a net gain.
Increased Property Value
Properties with standard and off-grid systems are often valued higher than those without. Buyers are willing to pay a premium for homes with sustainable energy solutions due to the long-term savings and environmental benefits. This increase in property value can provide a return on investment for homeowners who install solar systems.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Solar power systems require minimal maintenance compared to traditional energy systems. With no moving parts, solar panels are less prone to wear and tear. Regular cleaning and occasional inspections are usually sufficient to keep the system operating efficiently. The reduced maintenance costs contribute to the overall financial benefits of solar energy.
Practical Considerations


Before installing a solar or off-grid system, several practical considerations need to be addressed:
Site Assessment
A site assessment is crucial to determine the suitability of a location for solar panel installation. Factors such as roof orientation, shading, and available space influence the efficiency of the solar system. A professional assessment can provide insights into the optimal placement and potential energy production of the system.
System Sizing
Proper sizing of the solar and battery system is essential to meet energy needs. An undersized system may not provide sufficient power, while an oversized system can lead to unnecessary costs. An energy audit can help determine the appropriate system size based on current and future energy consumption patterns.
Installation Costs
The installation cost of solar and off-grid systems varies based on factors such as system size, location, and available incentives. It is important to obtain multiple quotes from reputable installers and consider the long-term savings when evaluating the cost.
Regulatory Requirements
Local regulations and building codes may impact the installation of solar and off-grid systems. Permits and inspections are often required to ensure compliance with safety standards. Understanding and adhering to these requirements is essential for a successful installation.
Conclusion


Solar and off-grid solutions offer a viable path to reducing energy costs and achieving energy independence. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems provide sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions for homes and businesses.







