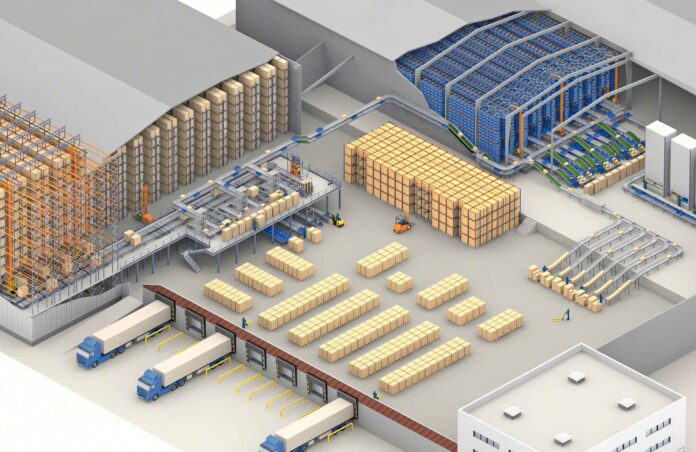
Warehouse layout optimization is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency.
Besides proper gear, which you can find at lenokers.com, you also need to think about the ways to optimize what you have to enhance productivity.
A well-optimized layout boosts workflow, reduces shipment times, and maximizes space utilization.
Types of Warehouse Layouts


First, let us address different layouts.
U-Shaped Warehouse
A U-shaped warehouse layout is characterized by the arrangement of the warehouse’s main activities in a U-formation.
The receiving and shipping areas are typically located on opposite sides of the U, with storage and picking zones in the middle. This design creates a smooth flow of goods from receiving to shipping, minimizing handling and travel distances.
The U-shaped layout offers several benefits. It maximizes space utilization by using the warehouse’s perimeter for storage and central areas for handling activities.
It is particularly beneficial for warehouses with high throughput and frequent shipments, as it facilitates quick and efficient movement of goods. It is ideal for warehouses that handle a diverse range of products and require flexibility in handling different types of inventory.
The U-shaped design also allows for easy supervision and management, making it suitable for smaller to medium-sized warehouses with moderate to high-volume operations.
L-Shaped Warehouse
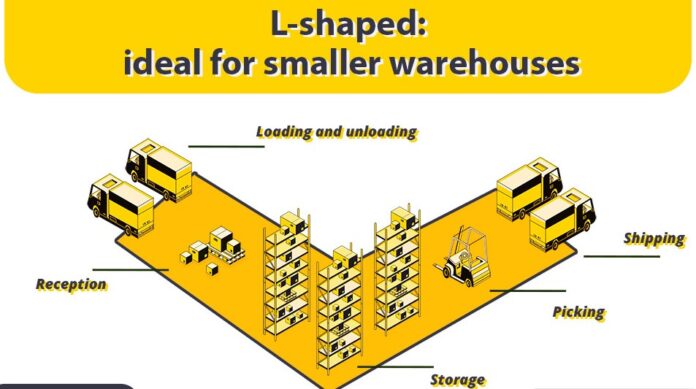

An L-shaped warehouse layout arranges the main warehouse functions along the two arms of an L-shape. Typically, one arm is designated for receiving and storage, while the other arm is used for picking and shipping activities. It separates the inbound and outbound processes, creating a clear division of space and tasks.
The L-shaped layout provides several advantages. It allows for a clear separation of receiving and shipping areas, reducing congestion and improving workflow efficiency. This layout is beneficial for warehouses with distinct inbound and outbound processes, as it minimizes the risk of cross-contamination and ensures smooth operations.
It is particularly suitable for facilities with limited space, as it efficiently utilizes corner areas that might otherwise be underutilized. The L-shaped design is ideal for warehouses that handle a moderate volume of goods and require distinct areas for different operations.
I-Shaped Warehouse


An I-shaped warehouse layout, also known as a straight-line layout, arranges all warehouse activities in a linear fashion. The receiving area is located at one end of the warehouse, with storage and picking zones in the middle, and the shipping area at the opposite end.
The I-shaped layout offers several benefits. It creates a clear, linear flow of goods, minimizing the risk of bottlenecks and congestion. This layout is ideal for warehouses with high-volume operations and a straightforward product flow.
It is particularly beneficial for facilities with automated systems, as the linear design supports efficient automation and material handling.
The I-shaped layout is suitable for warehouses that handle a large volume of goods with a simple and consistent flow, such as distribution centers and e-commerce fulfillment centers.
Steps to Optimization
Next, we would like to talk about the steps to optimization.
Analyze Current Warehouse Throughput
Analyzing the current throughput of a warehouse is crucial for identifying areas that need improvement.
By assessing the performance of existing operations, businesses can gain insights into inefficiencies and bottlenecks that hinder productivity. This analysis helps in making informed decisions about layout changes and optimizing workflows to enhance overall efficiency.
There are various tools and methods available for analyzing warehouse throughput. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) provide real-time data on inventory levels, order processing times, and worker productivity.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as order fulfillment rates, picking accuracy, and cycle times can be used to measure performance and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, time and motion studies can be conducted to assess the efficiency of specific tasks and processes.
By leveraging these tools and methods, businesses can obtain a comprehensive understanding of their warehouse operations and make data-driven decisions to optimize layout and improve throughput.
Study Product Needs
Assessing Product Types and Business Requirements:
Understanding the specific needs of the products stored in the warehouse is essential for optimizing the layout.
Different products have varying storage requirements, handling procedures, and safety considerations.
By assessing the types of products and their business requirements, businesses can determine the most suitable storage systems and layout configurations to meet these needs.
Considerations for Specific Product Needs:
Certain products may require specialized storage conditions, such as temperature-controlled environments, hazardous materials handling, or value-added services (VAS) stations for labeling and packaging. It is important to consider these specific needs when designing the warehouse layout.
Safety conditions, such as fire prevention measures and emergency exits, should also be taken into account.
By tailoring the layout to the unique requirements of the products, businesses can ensure efficient storage, handling, and retrieval, minimizing the risk of damage and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Importance of Warehouse Layout Optimization

Optimizing warehouse layout is pivotal in maintaining a streamlined workflow and maximizing productivity.
An efficient layout ensures that products are stored in a manner that allows for easy access and retrieval, significantly reducing the time taken to fulfill orders.
This efficiency translates into faster turnaround times for shipping and receiving, directly impacting customer satisfaction and the overall performance of the business.
By strategically organizing the warehouse, businesses can minimize the distances that workers need to travel, thereby increasing overall efficiency and reducing labor costs. For instance, placing high-frequency items closer to the shipping and packing areas reduces the time employees spend walking, leading to faster order fulfillment.
This strategic placement of inventory is known as slotting, and it is an essential aspect of warehouse layout optimization. Slotting can be periodically reviewed and adjusted based on changes in demand patterns, ensuring that the warehouse continues to operate at peak efficiency.
Moreover, an optimized layout facilitates better inventory management, making it easier to track stock levels and reduce the chances of overstocking or stockouts. With clearly defined storage zones and systematic organization, businesses can implement more effective inventory control measures.
Technologies such as barcode scanning, RFID tags, and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) can be seamlessly integrated into an optimized layout, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and streamlining stock management processes.
The Bottom Line


Optimizing warehouse layout is essential for improving efficiency, reducing shipment times, and enhancing workflow. Continuous optimization ensures sustained operational excellence and adaptability to future growth.